A 1-month-old infant is brought to the emergency department after he had a coughing spell while feeding and turned blue. His mother says that the blue color went away when she picked him up and brought his knees to his chest. Chest X-ray reveals a boot-shaped heart. The mother is told that he has a condition caused by an anterosuperior displacement of the infundibular septum.
(1) Name this congenital cardiac defect.
(2) What are the 4 features of the baby’s cardiac condition?
Tetralogy of fallot
This Post Has One Comment
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.

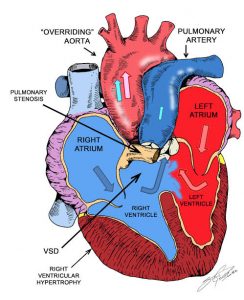
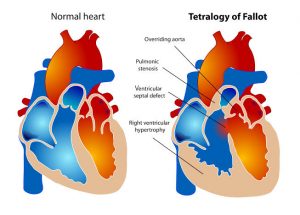
Tetralogy of Fallot is a congenital heart defect that has 4 main features: pulmonary stenosis, right ventricular hypertrophy, ventricular septal defect (VSD), and an overriding aorta.
These features arise due to an anterosuperior displacement of the infundibular septum of the heart. The right ventricular hypertrophy results in a right-to-left shunt that sends deoxygenated blood through the VSD and into the body. This right-to-left shunt results in cyanosis and a ‘tet’ spell.
Older patients will often squat down to increase systemic vascular resistance and reverse the shunt. Patients can also present with failure to thrive and problems with feeding shortly after birth. The initial investigation can include a chest X-ray, which shows the characteristic boot-shaped silhouette of the heart that is due to right ventricular hypertrophy.
Definitive treatment is surgical because there is a 50% mortality rate by 6 years of age and a 90% mortality rate by 20 years of age if left untreated.